
Network switches mainly operate at layer 2 as well as layer 3 switches. Layer 3 switches combine layer 2 and layer 3 capabilities I’ll be going over mostly layer 2 switch functions for this post. Switch come in 2 different forms such as managed switches and unmanaged switches. unmanaged switches are unable to configured and are plug and play used for basic network needs while managed switches are able to be fully configured. Switches are used to connect all devices to the network such as computers, VOIP Phones, servers, printers and other network devices. Switches interfaces operate at full-duplex mode which breakup collision domains with each interface.
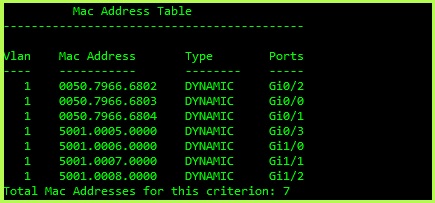
Traffic moves between a switch basic of MAC addresses that are stored in a MAC address table switches learn the MAC address when a frame enters the switch and associates it the interface it is connected to, the MAC address by default is stored in the MAC address table for 300 seconds (5 Minutes) if there is no traffic on the interface that it is attached to. The switch forward frames based on to the destination MAC address and forwards it out the interfaces that matches the interface address in the MAC address table. If the switch does not know the MAC address of the destination address, it sends out a broadcast to every port on the switch expect for the interface the frame was received. The image blow shows an example of an MAC Address table on from a Switch.
Management switches that can be configured as different features that can be configured such as VLANs, STP (Spanning Tree protocol), Link Aggregation and Quality of Service.
VLAN – Virtual Local Area Networks: VLANs allow switches to segment traffic on the same switch, VLANs are not able to communicate with other VLANS unless allowed by a router or layer 3 switch. VLANs are used to break up broadcast traffic and are also used for separating different types of traffic such as VOIP, Data, Management traffic which helps with improve network security. See image below for a basic example of VLANS

STP – Spanning Tree Protocol: STP is used to prevent loops when multiple switches are connected, STP stops broadcast storms from flooding the network, this is done by blocking redundant paths while still providing connectivity. If the primary fails STP will activate a secondary path. There are different mods of STP such as RSPT (Rapid Spanning Tree), PVST+ (Per-VLAN Spanning Tree), RPVST+ (Rapid Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Plus), and MST (Multiple Spanning Tree Procol).
QoS – Quality of Service: QoS is used to prioritize different types of traffic such as voice, video, data, network management etc. to reduce latency for critical traffic, example would be to prioritize video and voice traffic so that there is no noticeable lag or breaking up in a video or voice call and setting lower priority to network management traffic.
Link Aggregation – Link Aggregation or EtherChannel is used to bundle physical interfaces to a single logical interface using protocols such as LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) or PAgP Port Aggregation Protocol. Link Aggregation is used to provide redundancy as increase bandwidth by combining 2x 1 gigabyte interface int to a logical 2 gigabyte interface. Configuring Link Aggregation can sometimes cause problems with voice packets arriving out of order and making the call sound broken up.

Some switch interfaces provide PoE (Power over Ethernet) to provide power to devices such as VOIP phones, security cameras, access points and other IOT devices. There are different PoE types that provide different power outputs.
Switches are a huge part of everyday network whether it comes to your home network with connecting a few security cameras to large offices connecting 1000s of devices as well as data centers running in a spine and leaf architecture. There are more in depth post I can go in to on some of switching such as breaking down VLANS and how they are configured as well as STP and Link Aggregation, there’s a few other features in a switch that I did not mention that I can discuss such as interface mirror and why you would want to do that in your network for monitoring and troubleshooting or let me know if there’s anything more about switches you’d let me go into more in-depth information about.
Leave a comment