Network Topology Architectures has a few different designs such as three-tier, two-tier / collapsed core, spine-leaf mainly for data centers, small office/home office (SOHO), and on-premises/cloud. One of the reasons these make complicated large networks less completed and give them more of a hierarchy design.

Three-Tier Architecture
Three-Teir Architecture design works well for large enterprise networks as well as ISP environments,
They help make complex networks easier to manage, allow easier scalability making adding devices/upgrading easier. Also, more reliable with more layers of redundancy and better performance. The draw backs are cost, and it does make the network more complex. The Three-Teir consist of 3 layers the core, distribution and access layers
Core Layer – the core layer is the backbone of the network, connects to the ISP, connects to other branch offices. Core Layer would be configured with Routing Standby protocols. The Core layer has multiple connection to the distribution layer This is where high end devices would operate.
Distribution layer – This layer provides communication between the access layer and the core layer. This layer has redundancy build in for the access layer switches and to the core layer. The distribution layer applies access-lists and QoS policies.
Access Layer – The access layer is where all the users and end devices such as computers, phones, printers, servers, access points, etc., are connect to the network. This layer allows users to share data and resources within internal the network through the distribution layer. Network segmentation happens at the access layer with VLANs.
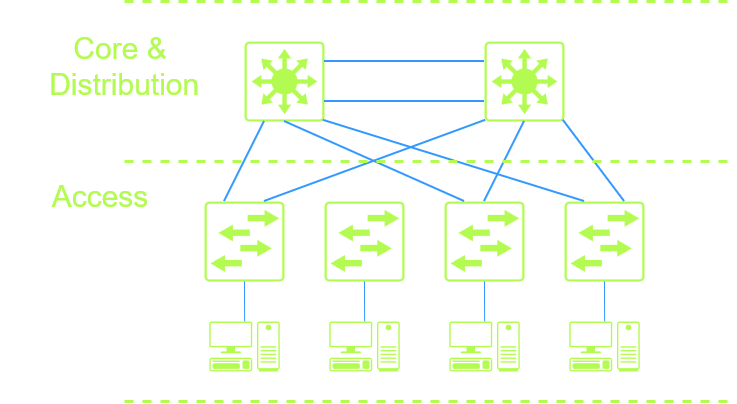
Two-Tier
The two-tier design also known as a collapsed core, the core and the distribution layers are combined. This design good for smaller networks and is more cost efficient with eliminating the core layer. The Core and distribution layer functions as both the core and distribution layers in the two-tier design. Two-tier design still allowed scalability and easier expansion as well as redundancy.
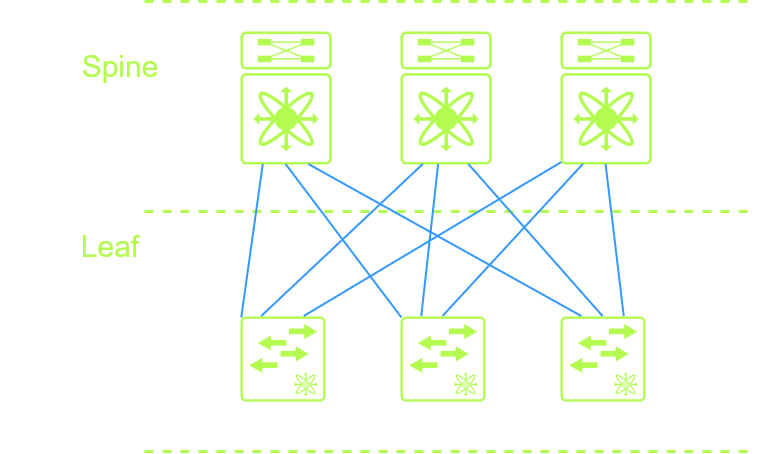
Spine-Leaf Architecture
Spine-Leaf Architecture – is modern design that is for data centers, AI, and cloud environments, this is for very high bandwidth and high performance, with little hop count between devices. This design creates a full mesh allowing for easy scalability allowing to add more spine and leaf switches if as needed. This design is more costly and is normally managed by Cisco DNA center now called Cisco Catalyst Center using an overlay and underlay network. You will see mostly Cisco nexus devices at the spine and leaf design.
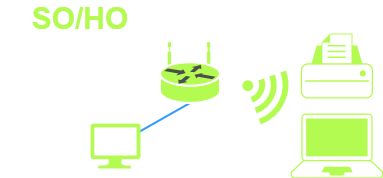
small office/home office is a flat network sometimes just the internet modem/router that your ISP provides, in other cases with a firewall/router and switch and a device that provides wireless. SO/HO have a small number of end users and devices such as computers, laptops printers. SO/HO are not as costly and can be plug and play and does not require much administration.

on-premises is when all networking, servers, storage, and software is located locally on site. Everything falls on the local IT team to manage. Start up costs are higher such as space for networking devices, power, cooling and maintenance, physical security is required as well as Disaster recovery. This is used a lot for sensitive data such as healthcare or financial.
Cloud is hosted at places such as AWS or Azure and can be based on a pay as you need allowing to spin up and turn down different services during high traffic times if required. Disaster recovery is done by the cloud provider, also security relies on the provider as well leaving a chance for some risk.
Leave a comment